What is Thalassemia?
Thalassemia is a genetically inherited blood disorder which directly affects the production of haemoglobin protein. Haemoglobin is a very essential protein that is required by the body to have a healthy production of red blood cells. In patients who suffer from various kinds of thalassemia, the red blood cells will be less in production and the ones produced will not complete its complete life cycle.
Thalassemia can also manifest in various types one of which is very severe and is called Cooley’s Anemia. In order to understand thalassemia better, you should understand the details of how blood is produced in the body. Haemoglobin is the protein that is responsible for the oxygen-carrying properties of the red blood cells. Alpha haemoglobin and beta haemoglobin are both responsible for carrying out these functions with ease. If there is any sort of inefficiency in the functioning and production of these proteins it will lead to the condition called as thalassemia. In extreme cases, thalassemia can be deadly if not treated at the right time.
Most of the common symptoms are:
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Pale or yellow skin tone
- Delayed growth
- Bone deformities
- Dark urine
Types of Thalassemia:
- Alpha Thalassemia
- Beta Thalassemia
- Other
Alpha Thalassemia:
Alpha thalassemia is a condition where the production of alpha globins for the red blood cells are reduced. Alpha thalassemia is also a genetic disorder coming from the genes of both parents. Alpha thalassemia is most prevalent in the regions of Africa, South East Asia, India, South of China and also rarely in the Mediterranean regions.
There are four subcategories of Alpha Thalassemia:
Silent Carrier State:
This is a form of alpha thalassemia where little or no symptoms will be exhibited by the person affected, hence the name silent carrier. The alpha globin production will be low but will rarely have even mild physical implications. These patients are however carriers of the mutated genes and can cause thalassemia to their offsprings.
There are different variations of silent carrier state:
-
Haemoglobin Constant Spring:
This is a subcategory of silent carrier state and resembles most of the symptoms. It is caused due to the mutation that happens to the alpha globin. The strange name comes from the region in Jamaica where it was first discovered.
-
Alpha Thalassemia Trait:
This is a mild format of thalassemia where the gene mutation is present. The patients will have red blood cells that are smaller in size and will also suffer from mild anaemia. The lack of alpha protein can be minimal and therefore no blood transfusion will be required. In most cases, the medical practitioner diagnosing the case may misdiagnose alpha thalassemia trait as anaemia and prescribe medication that will have no effect of increasing the count of the red blood cells.
-
Haemoglobin H Disease:
Haemoglobin H disease is a bit more severe form of alpha thalassemia, the reduction of the gene is high causing conditions like an enlarged spleen and bone deformities. The name comes from the excess of the unwanted haemoglobin H that is capable of destroying the healthy red blood cells. There are other subcategories of Haemoglobin H Disease.
-
Haemoglobin H Constant Spring:
This blood disorder is considered to be more severe compared to the parent category. In this condition, the patient will have visible symptoms of anaemia and enlarged spleen and the patient will also be susceptible to viral infections. Homozygous Constant Spring: This blood disorder occurs when infants both parents suffer from Haemoglobin H Constant Spring. This condition is less severe than the above subcategories and the symptoms resemble that of haemoglobin H disease. Alpha Thalassemia Major: This blood disorder also goes by the name Hydrops Fetalis. The condition is caused due to the complete absence of alpha protein in the blood cells. This leads to the presence of gamma proteins which aids in the production of the malfunctioning protein called as Haemoglobin Barts. This type of thalassemia affects the fetus and most of the children who suffer from this condition will be stillborn.
The new advancements in thalassemia medication have led to treatment option that can be availed called Utero Blood Transfusion, however, the children who are born with alpha thalassemia major will have to get blood transfusion treatments throughout their lives to continue staying alive.
Beta Thalassemia:
Beta Thalassemia is when the genes inherited from mother and father which aids in the production of beta-globin is mutated. The HBB gene is responsible for the production of beta-globin and two sets have to be inherited from both the parents.
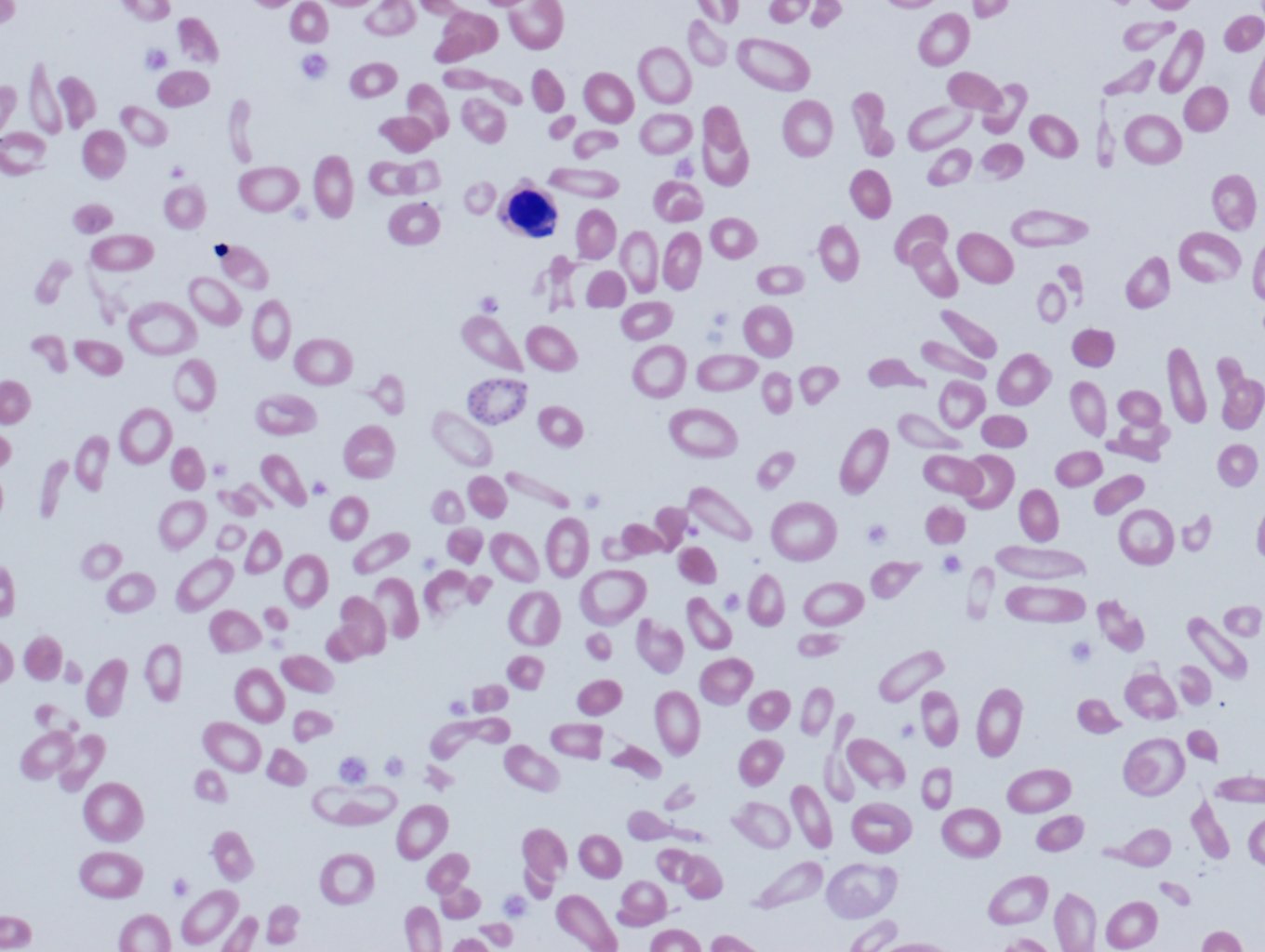
There are three sub-categories under beta thalassemia:
-
Thalassemia Major:
This form of thalassemia is commonly called as Cooley’s anaemia. This condition is more prevalent in the people who have origins from the Mediterranean regions including Italians, Arabs, Greeks, Africans, Chinese and the people from south-east Asia. This form of thalassemia shows symptoms right after two years of childbirth. The anaemia associated with thalassemia major is dangerous and can cause a serious threat to the health of the patient. Most often since the condition is so severe that the patient is required to undergo blood transfusions at a small age.
-
Thalassemia Minor:
This condition is a comparatively less severe form of thalassemia. It occurs due to mutation caused to both the genes and the person affected may not show any symptoms. However, patients with thalassemia intermediate are carriers of the mutation and the offsprings of theirs will be at risk of thalassemia. This condition is also known as thalassemia trait.
-
Thalassemia Intermediate:
In this condition, the severe lack of beta-globins may not be there yet there are high possibilities of having moderately severe anaemia, accompanied with bone deformities and an enlarged spleen. The condition may require regular blood transfusions for the affected person to continue having a normal lifestyle.
Other Types of Thalassemia:
Apart from alpha and beta thalassemias, there are other rare possible types of thalassemia which occurs when these genes tend to combine with other genes that are also mutated. Some of the other forms of thalassemias are listed below.
-
E-Beta Thalassemia:
This condition is caused when Haemoglobin E, which is a very common form of abnormal haemoglobin usually found in people from the regions of Indonesia, Cambodia, Vietnam and Thailand, combines with the mutated genes causing beta-thalassemia. This condition has symptoms almost similar to that of intermediate beta thalassemia.
-
Sickle Beta Thalassemia:
Sickle beta thalassemia is a condition that is caused by the presence of Haemoglobin-S which is the abnormal protein that is present in people suffering from sickle cell anaemia. When combined with beta-thalassemia this can cause anaemic results and lower red blood cell count.
Treatments for Thalassemia:
Even though thalassemia is a condition that can cause severe disabilities in the normal lifestyle of a person, there are various treatment methods that are used to curb the symptoms of the same. The whole condition cannot be cured completely since it is a genetic disorder, however, with advanced research in stem cell therapy, there is a significant amount of hope for people who suffer from it.
The main methods used for the treatment of thalassemia 1 are listed below:
-
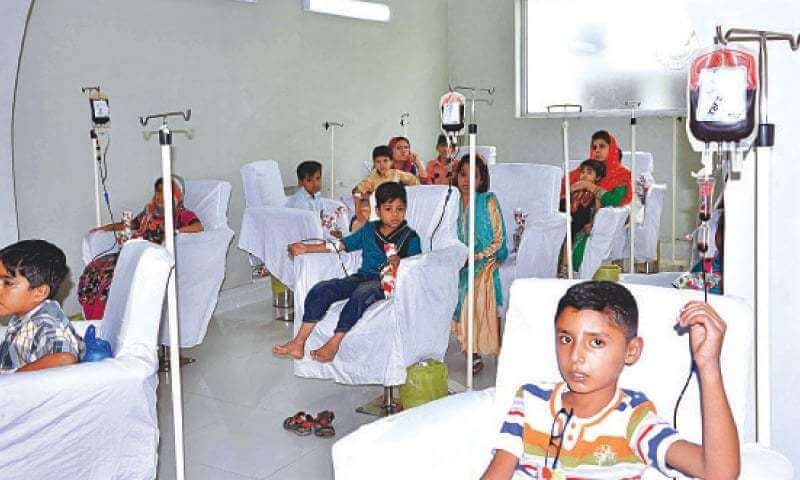
Blood Transfusions:
Blood transfusion is the oldest and safest treatment method for thalassemia. This is done by medical practitioners based on the type and severity of your condition. Healthy red blood cells are provided to the body through plastic tubes to the blood vessels. This can reduce the anaemia and the vital organs will be replenished with the necessary oxygen and minerals. The frequency of the blood transfusion is entirely dependant on the type of thalassemia with regular transfusion required for patients suffering from thalassemia major both alpha and beta.
-
Bone Marrow Transplants:
Bone marrow transplants for thalassemia is a still in its experimentative stages. The process works on the logic that most of the blood production happens in the bone marrow. The genetic malfunctioning will affect the blood marrow and transplanting this with healthy bone marrow will help in reducing the severity of the symptoms.
-
Medications:
Medications that are aimed at reducing the anaemia are also prescribed by doctors as a part of the treatment plan for thalassemia. The doctors usually prescribe vitamin B supplements and folic acid to help combat the anaemia.

Thalassemia is a major blood disorder that requires continuous medical attention. Different part of the world suffers from different types of anaemia. It’s essential that you are well educated about the severity of the condition so that you can combat it with the help of your friends and family.